In this tutorial, you will learn input and output operations in Python with clear examples and explanations. You will also practice pattern-based questions in Python to improve logic building and prepare for interviews. In previous tutorial we seen control statement
When learning Python programming, one of the first things beginners encounter is input and output operations in python. These concepts are essential because they allow interaction between the program and the user.
For example, when creating pattern programs like pyramids or diamonds, you need to take user input for rows or symbols and display structured output.
A) Input and Output
How to display output using print()?
How to take user input using input()?
Converting inputs to numbers?
Writing nested loops to create popular pattern programs such as pyramids and diamonds
Tricks to understand loops easily
1) Displaying Output with print()
The print() function in Python is used to show messages, results, or values to the user. It’s the most basic function for output operations.
Syntax
print(object1, object2, …, sep=’ ‘, end=’\n’)
Explain
object1, object2 → Values or text to display.
sep → Separator between multiple values (default is a space ” “).
end → Character printed at the end (default is a newline \n).
Examples
Example 1: Basic Output
print(“Hello, Python!”)
Output:
Hello, Python!
Example 2: Printing Multiple Values
print(“My name is”, ” James”, “Robert”)
Output:
My name is James Robert
Example 3: Using sep and end
print(“Python”, “is”, “fun”, sep=”-“, end=”!!!”)
Output:
Python-is-fun!!!
💡 Trick to Remember:
output operation
Think of print() as “sending a message to the screen.”
2) Taking User Input with input()
input operation
The input() function allows you to get data from the user while the program runs.
By default, everything entered is stored as a string.
Syntax
variable = input(“Enter your message: “)
Explain
variable → Stores the user’s response.
The message inside input() acts as a prompt for the user.
Examples:
Basic Input Operation
name = input(“Enter your name: “)
print(“Hello,”, name)
output:
Enter your name: James
Hello, James
3) Converting Input to Numbers
input operation
Since input() returns a string, you need to convert it into integers or decimals for calculations.
Example: Adding Two Numbers
num1 = int(input(“Enter first number: “))
num2 = int(input(“Enter second number: “))
result = num1 + num2
print(“The sum is:”, result)
Output:
Enter first number: 5
Enter second number: 7
The sum is: 12
B) pattern-based questions in Python
When writing pattern programs, we typically take the number of rows and columns as input.
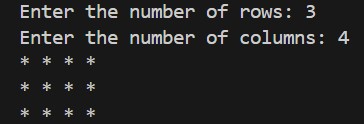
- Example: Printing a 3×4 Star Grid
rows = int(input(“Enter the number of rows: “))
cols = int(input(“Enter the number of columns: “))
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
print(“*”, end=” “)
print()
Output (if rows=3 and cols=4):
Explanation:
- Variables
rows = 3 → total rows in the grid.
columns = 4 → total stars in each row.
- Loops
Outer loop (for i in range(rows)):
Runs 3 times → one for each row.
Inner loop (for j in range(columns)):
Runs 4 times per row → prints 4 stars in that row.
- Print Statements
print(“*”, end=” “) →
Prints * and stays on the same line.
end=” ” adds a space instead of a newline.
print() → Moves to the next line after finishing one row.
Nested Loops and Pattern Printing
In pattern matching question the, Nested loops are loops inside another loop.
They are the backbone of creating pattern programs because they allow you to manage rows and columns separately.
💡 Trick:
Outer Loop → Row
Inner Loop → Columns / Elements inside the row
Popular Pattern Programs in Python
Here are some popular pyramid pattern programs along with step-by-step solutions and logic.
Here are some popular pyramid pattern programs along with step-by-step solutions and logic.
- Simple Star Pyramid
This is the most basic pyramid pattern.
Expected Output:

Code:
rows = int(input(“Enter number of rows: “))
for i in range(1, rows + 1):
for space in range(rows – i):
print(” “, end=””)
for star in range(i):
print(“* “, end=””)
print()
💡 Trick:
Spaces decrease, stars increase with each row.
Formula:
Space = Total Rows – Current Row
Stars = Current Row
2.Inverted Pyramid
Expected Output

Code:
rows = int(input(“Enter number of rows: “))
for i in range(rows, 0, -1):
for space in range(rows – i):
print(” “, end=””)
for star in range(i):
print(“* “, end=””)
print()
💡 Trick:
Reverse the loop for stars.
Spaces increase, stars decrease.
3. Right-Aligned Half Pyramid
A right-angle triangle pattern is one of the simplest and most common programming patterns.
It forms a triangular shape where:
The right angle (90°) is at the bottom-left corner.
Each row contains increasing numbers of stars (*) or numbers, starting from 1 in the first row.
Expected Output:

Code:
rows = int(input(“Enter number of rows: “))
for i in range(1, rows + 1):
print(” ” * (rows – i) + “*” * i)
💡 Trick:
” ” * (rows – i) → Spaces
“*” * i → Stars
Pattern Matching question on Numbers
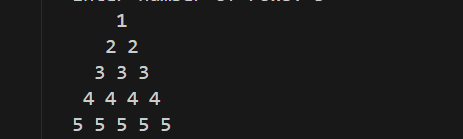
- Number Pyramid
A number pyramid is a pattern in which numbers are arranged in the shape of a pyramid.
Each row contains numbers in a specific sequence, with proper spacing to keep the structure centered.
Expected Output:
Code:
rows = int(input(“Enter number of rows: “))
for i in range(1, rows + 1):
for space in range(rows – i):
print(” “, end=””)
for num in range(i):
print(i, end=” “)
print()
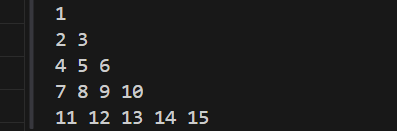
5.Floyd’s Triangle
Floyd’s Triangle is a simple number pattern built row by row using consecutive integers.
Expected Output:
code:
rows = int(input(“Enter number of rows: “)) # User enters how many rows to print
num = 1
for i in range(1, rows + 1):
for j in range(i):
print(num, end=” “)
num += 1
print()
💡 Trick:
Use a variable to track numbers across rows.
6. Diamond Pattern
A diamond star pattern is a symmetric arrangement of stars (*) that resembles the shape of a diamond.
It is one of the most common problems for beginners in programming to practice nested loops, conditional statements, and string manipulation.
Example Output:

Code:
rows = int(input(“Enter number of rows: “))
—upper half
for i in range(1, rows + 1):
print(” ” * (rows – i) + “* ” * i)
—lower half
for i in range(rows – 1, 0, -1):
print(” ” * (rows – i) + “* ” * i)
💡 Trick:
Combine normal pyramid + inverted pyramid.
Summary Table of Patterns:
Pattern Spaces Stars/Numbers
Normal Pyramid rows – i i
Inverted Pyramid rows – i i (reverse loop)
Right-Aligned Half rows – i i
Number Pyramid rows – i Print number i
Diamond Pattern Combine Normal + Inverted Combine both
Conclusion
Understanding basic input/output operations and nested loops is essential for building logic in Python.
By practicing these pattern programs, you will:
Improve problem-solving skills
Strengthen your understanding of loops
Build a strong foundation for advanced Python programming