Introduction
When you first start learning Python, lists quickly become one of your favorite tools, here we will learn python list methods.
They’re flexible, powerful, and perfect for storing collections of items like numbers, strings, or even other lists.
But mastering Python list methods — especially append(), remove(), and pop() — is what separates a beginner from a confident coder.
In this article, we’ll explore these top three Python list methods in depth — with code examples, real-world analogies, and common pitfalls to avoid. By the end, you’ll handle lists like a pro.
What Are Python List Methods?
A list method in Python is a built-in function that lets you modify or access elements in a list.
Think of it as a special ability that helps lists behave dynamically — you can add, delete, or extract elements without rewriting the whole list.
Some popular list methods include:
append()– Add an element at the endremove()– Delete the first occurrence of a valuepop()– Remove an element by its indexinsert(),sort(),reverse(),extend(), and many more
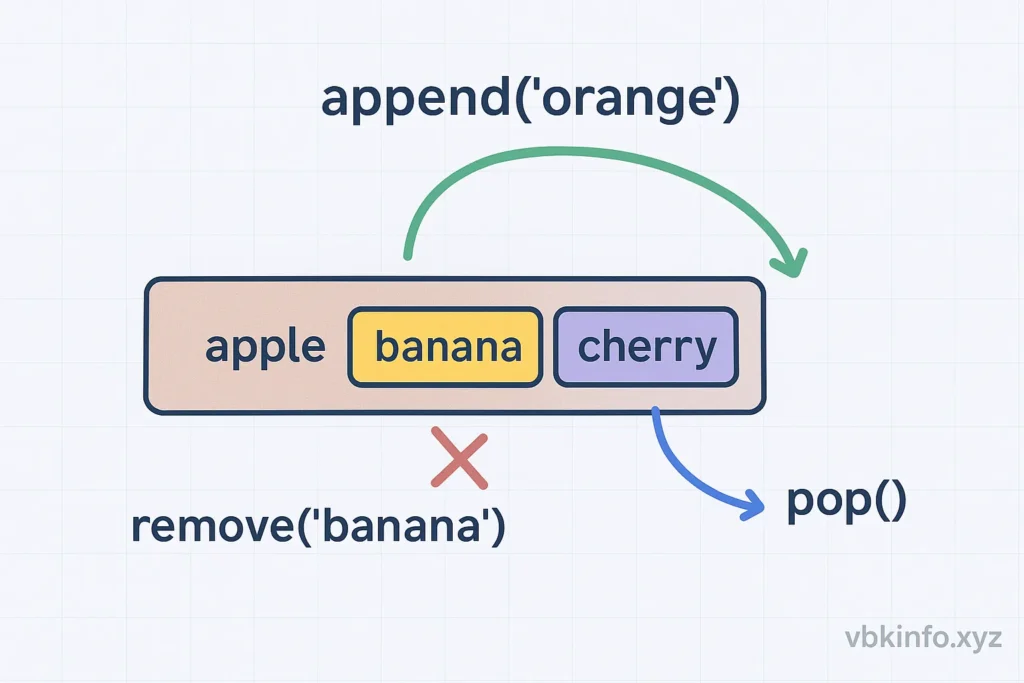
Append(), Remove(), and Pop() — The Core Trio
append() Method Explained
Syntax:
list.append(item)The append() method adds an element to the end of the list. It modifies the original list in place.
Example:
fruits = ["apple", "banana"]
fruits.append("cherry")
print(fruits)Output:
['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']When to use:
Use append() when you want to grow a list — for instance, while collecting user input or storing API results dynamically.
remove() Method Explained
Syntax:
list.remove(value)
The remove() method deletes the first occurrence of the specified value.
Example:
numbers = [10, 20, 30, 20, 40]
numbers.remove(20)
print(numbers)
Output:
[10, 30, 20, 40]
🔹 When to use:
Use remove() when you know the value you want to delete but not its index.
Error Alert:
If the value doesn’t exist, Python raises a ValueError. Always check with if value in list: before removing.
pop() Method Explained
Syntax:
list.pop(index)
The pop() method removes the element at a given index and returns it.
If no index is provided, it removes the last item by default.
Example:
colors = ["red", "green", "blue"]
removed = colors.pop(1)
print(colors)
print("Removed:", removed)
Output:
['red', 'blue']
Removed: green
🔹 When to use:
Use pop() when you need to access and remove an element simultaneously — for example, when processing a stack or queue.
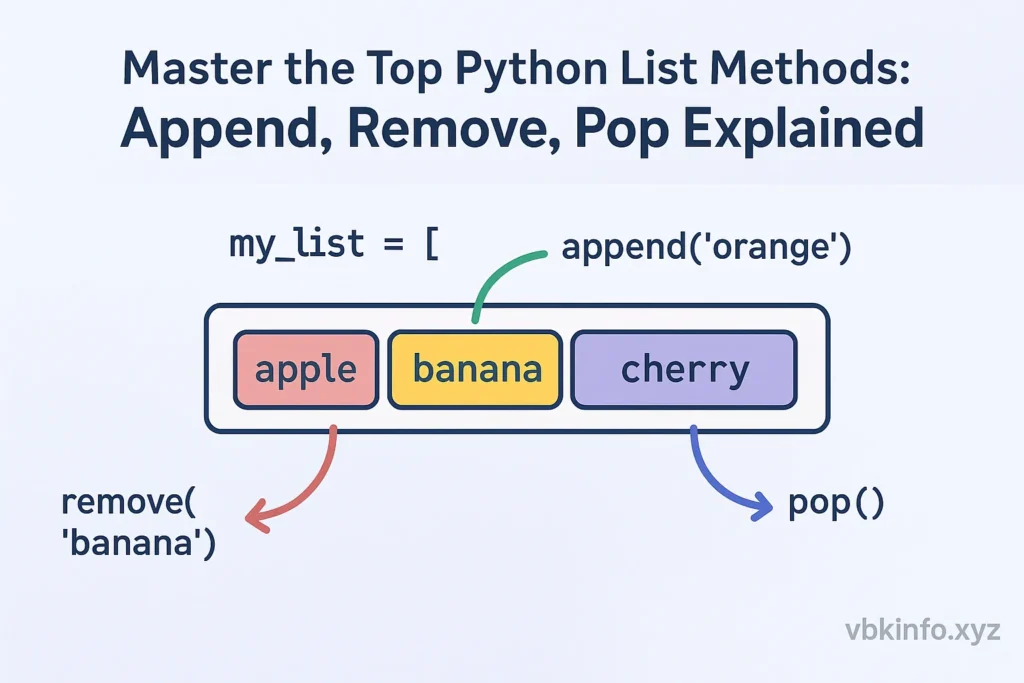
Code Examples for Each Method
Let’s explore how these three methods can work together.
# Example: Student attendance system
students = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"]
# 1. A new student joins
students.append("Diana")
print("After append:", students)
# 2. A student leaves
students.remove("Bob")
print("After remove:", students)
# 3. The last student signs out
signed_out = students.pop()
print("After pop:", students)
print("Signed out student:", signed_out)Output:
After append: ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'Diana']
After remove: ['Alice', 'Charlie', 'Diana']
After pop: ['Alice', 'Charlie']
Signed out student: DianaReal-World Analogy: Lists as Dynamic Buckets
Imagine your list as a bucket holding different fruits.
- append() – You add a new fruit to the bucket.
- remove() – You take out a specific fruit by name.
- pop() – You pull out a fruit by position (maybe the last one you added).
This bucket analogy helps you visualize how Python manages elements behind the scenes — efficiently and dynamically.
Common Mistakes and Best Practices
1. Forgetting remove() only deletes the first match
nums = [2, 2, 2]
nums.remove(2)
print(nums) # Only one 2 removed
✅ Tip:
Use a list comprehension if you want to remove all occurrences:
nums = [n for n in nums if n != 2]
2. Using pop() without checking list length
If you pop() an empty list, Python throws an IndexError.
✅ Fix:
if my_list:
my_list.pop()
3. Chaining methods incorrectly
Remember that these methods modify lists in place and return None.
So avoid:
print(my_list.append(5)) # Outputs None
✅ Correct:
my_list.append(5)
print(my_list)Comparison Table: append vs remove vs pop
| Method | Adds/Removes | Requires Value or Index | Returns Value | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| append() | Adds item | Value to add | No | Add data dynamically |
| remove() | Removes item | Value | No | Delete by value |
| pop() | Removes item | Index (optional) | Yes | Retrieve and delete item |
FAQs: Python List Methods
1. What is the difference between append and extend in Python?
append() adds a single element to the list, while extend() adds multiple elements from another iterable.
a = [1, 2]
a.append([3, 4]) # [1, 2, [3, 4]]
a.extend([3, 4]) # [1, 2, 3, 4]
2. What happens if I remove a value that doesn’t exist?
Python raises a ValueError.
You can avoid this with:
if value in my_list:
my_list.remove(value)
3. How can I delete multiple items from a list?
Use list comprehension or the filter() function:
nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 2]
nums = [n for n in nums if n != 2]
4. Which is faster — remove() or pop()?
pop() is generally faster since it operates by index (default last).remove() must first search for the value, making it slower for large lists.
Conclusion and Next Steps
The python list methods append(), remove(), and pop() are the foundation of effective list manipulation.
By understanding how each one works — and where they differ — you’ll write cleaner, faster, and more readable Python code.
Quick recap:
- Use append() to grow your list.
- Use remove() to delete by value.
- Use pop() to delete by index and retrieve the element.
✨ Next step: Practice combining these methods in small projects — like managing a to-do list or inventory app.
👉 Continue learning with these guides on vbkinfo.xyz:
External References:
Final CTA:
Did this guide help you master list methods? 💬 Drop a comment below or share your favorite Python trick with the vbkinfo.xyz community!
Want a free Python List Methods Cheat Sheet (PDF)? Subscribe to our newsletter today.
Final Words
Did this guide help you master list methods? 💬 Drop a comment below or share your favorite Python trick with the vbkinfo.xyz community!
Want a free Python List Methods Cheat Sheet (PDF)? Subscribe to our newsletter today.