“Welcome to the Python String Basics Tutorial, your step-by-step guide to mastering strings in Python. Strings are one of the most fundamental concepts in Python programming, used for everything from printing messages to building chatbots. so read the full tutorial Python String Basics Tutorial — Learn Step-by-Step with Examples.”.
Introduction: Why Learn Python Strings?
If you’re new to Python, one of the first concepts you’ll learn is Python String Basics Tutorial — Learn Step-by-Step with Examples. — sequences of characters that allow you to store, manage, and manipulate text efficiently. From printing messages and formatting user input to building chatbots, Python string methods and techniques are used in almost every Python project.
In this Python String Basics Tutorial, we’ll guide you step-by-step — covering everything from creating strings, indexing, and Python string slicing to advanced Python string formatting and manipulation. You’ll get practical examples, beginner-friendly explanations, and expert tips to avoid common mistakes.
By the end of this Python string tutorial for beginners, you’ll understand how Python strings work and how to use them effectively in real-world projects, making your code cleaner, faster, and more powerful.

What Is a String in Python?
In Python, a string is a sequence of characters enclosed within quotes. You can use single (‘ ‘), double (” “), or triple (”’ ”’ or “”” “””) quotes.
Definition (for snippet):
A string in Python is a sequence of Unicode characters enclosed in quotes used to represent textual data represent the below Step-by-Step with Examples.
# Creating strings in different ways
name = "Rahul"
greeting = 'Hello, World!'
multiline = """This is
a multi-line string."""
print(name)
print(greeting)
print(multiline)
Output:
Rahul
Hello, World!
This is
a multi-line string.
Strings are one of the most used data types in Python — flexible, powerful, and packed with built-in methods.
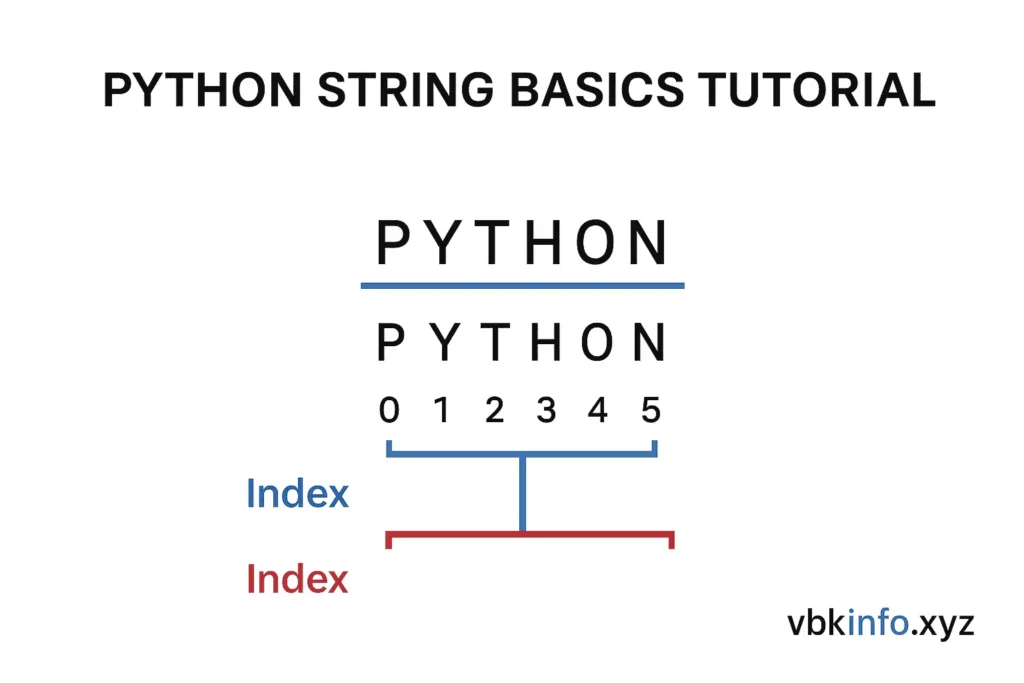
String Indexing and Slicing in Python
Just like lists, strings in Python are indexed. Each character has a unique index starting from 0.
text = "PYTHON"
# Accessing characters by index
print(text[0]) # P
print(text[3]) # H
# Negative indexing
print(text[-1]) # N
print(text[-3]) # H
String Slicing
You can extract parts of a string using the slicing syntax:string[start:end:step]
word = "programming"
print(word[0:6]) # progra
print(word[3:]) # gramming
print(word[:5]) # progr
print(word[::2]) # poramn
Tip:
Leaving start or end blank assumes the beginning or end of the string.
Common String Methods in Python
In Python strings basics the string have many built-in methods. Here are the most useful ones:
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|
upper() | Converts to uppercase | "hello".upper() → "HELLO" |
lower() | Converts to lowercase | "HELLO".lower() → "hello" |
strip() | Removes whitespace | " hello ".strip() → "hello" |
replace(a, b) | Replaces substring | "vbkinfo".replace("info", "blog") → "vbkblog" |
split() | Splits by separator | "Python,Java".split(",") → ['Python', 'Java'] |
join() | Joins sequence into a string | " ".join(['Learn', 'Python']) → "Learn Python" |
find() | Finds substring index | "python".find("th") → 2 |
Example:
msg = " Learn Python at vbkinfo.xyz "
print(msg.strip())
print(msg.upper())
print(msg.replace("Python", "Data Science"))
Output:
Learn Python at vbkinfo.xyz
LEARN PYTHON AT VBKINFO.XYZ
Learn Data Science at vbkinfo.xyz
String Formatting in Python
Formatting helps you combine variables and text seamlessly.
1. f-Strings (Python 3.6+)
name = "Rahul"
age = 25
print(f"My name is {name} and I am {age} years old.")
2. format() Method
text = "I love {0} because it's {1}."
print(text.format("Python", "easy to learn"))
3. Percentage (%) Formatting
lang = "Python"
version = 3.10
print("The latest version of %s is %.2f" % (lang, version))
Escape Characters in Strings
Escape characters let you include special symbols inside strings
| Escape Code | Description | Example Output |
|---|---|---|
\' | Single quote | 'It\'s Python' → It’s Python |
\" | Double quote | "He said, \"Hello\"" → He said, “Hello” |
\\ | Backslash | "C:\\Users\\Rahul" |
\n | New line | "Line1\nLine2" |
\t | Tab | "A\tB" |
Real-World Analogy: Strings as a Necklace
Think of a string as a necklace — each bead is a character. You can pick a bead by position (indexing), take a part of the necklace (slicing), or rearrange beads (string operations). This analogy helps beginners visualize how strings are structured and manipulated.
Tips, Tricks & Common Mistakes
✅ Tips
- Use triple quotes for multi-line strings or docstrings.
- Use
len()to find string length:len("Python") → 6. - Always prefer f-strings for readability.
❌ Common Mistakes
- Forgetting quotes around strings (
name = Vaibhav❌). - Modifying a string directly (strings are immutable).
- Using
+for large string concatenations — usejoin()instead for performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Are strings mutable in Python?
No. Strings are immutable — once created, you cannot change their characters.
Q2. How can I reverse a string?
Use slicing:
text = "vbkinfo"
print(text[::-1]) # ofnikbv
Q3. How to check if a substring exists?
Use the in keyword:
"info" in "vbkinfo.xyz" # TrueQ4. How to convert a string to a list?
Use list() or split():
list("Python") # ['P','y','t','h','o','n']
Comparison: String Formatting Techniques
| Technique | Syntax | Version | Readability | Recommended |
|---|---|---|---|---|
% | "Hello %s" % name | Old | Low | ❌ |
.format() | "Hello {}".format(name) | 3+ | Medium | ✅ |
f-string | f"Hello {name}" | 3.6+ | High | ✅✅✅ |
Real-World Use Case Example
Let’s say you’re creating a welcome email generator in Python:
user_name = "Rahul"
course = "Python Basics"
email = f"""
Hi {user_name},
Welcome to {course} at vbkinfo.xyz!
We're excited to help you learn step-by-step.
Happy Coding,
Team vbkinfo
"""
print(email)
Output:
Hi Rahul,
Welcome to Python Basics at vbkinfo.xyz!
We're excited to help you learn step-by-step.
Happy Coding,
Team vbkinfo
This example shows how string formatting and multi-line strings make your Python programs readable and maintainable.
Links for more clarity
Official Python String Documentation
W3Schools Python Strings Tutorial
and if you want to read the more about my tutorials then please check the below link
Python Variables Explained — Beginner Guide
Conclusion: Start Practicing Strings Today!
So in Python String Basics Tutorial — Learn Step-by-Step with Examples. the Strings are the foundation of text processing in Python. You learned how to create, slice, format, and manipulate them — plus some real-world tricks.
Now, it’s time to practice! Try writing your own small programs, explore advanced methods, and check out our next tutorials on Python String Functions and String Formatting in Depth.
What’s next?
Which string concept did you find most useful? Drop your thoughts in the comments below or share this tutorial with your friends learning Python!
Takeaway:
- Strings are sequences of text enclosed in quotes.
- Use slicing, indexing, and formatting to manipulate text efficiently.
- Strings are immutable — use methods like
replace()orjoin()for changes. - Mastering strings sets the foundation for Python mastery.
Keep learning at vbkinfo.xyz — your go-to platform for mastering Python step-by-step!