Introduction
If you’ve ever needed to search for a specific pattern, clean messy text data, or extract useful information from a webpage — regular expressions (regex) or python regex are your secret weapon. In this Python regex tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the re module effectively to manipulate strings with precision.
By the end of this guide, you’ll be able to:
- Recognize and write regex patterns for common use cases.
- Use Python’s
remodule functions likere.match(),re.search(), andre.sub(). - Solve real-world text processing challenges.
📋 Table of Contents
What is Python Regex?
Regular Expressions (Regex) are patterns used to match sequences of characters in text. In Python, the re module provides full support for regex operations.
Definition:
import re
pattern = r"[A-Za-z]+"
result = re.findall(pattern, "Hello World 123")
print(result)Output:
['Hello', 'World']Regex is like a powerful search language that recognizes patterns rather than fixed text.
Why Learn Regex?
- Efficiency: Replace manual text cleaning with single-line commands.
- Versatility: Suitable for emails, URLs, log files, datasets.
- Automation: Used heavily in web scraping, NLP, and system logs.
| Use Case | Example | Regex Pattern |
|---|---|---|
| Find email addresses | abc@gmail.com | [A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Za-z]{2,} |
| Extract phone numbers | +1-123-456-7890 | \+?\d{1,3}[- ]?\d{3}[- ]?\d{4} |
| Validate postal codes | 400001 | ^[0-9]{6}$ |
Python Regex Basics
Importing the re Module
Always start with:
import reKey Terminology:
- Pattern: The regex string you define, e.g.,
r"\d+"for digits. - Raw string (
r""): Prevents Python from treating\\as escape characters. - Match object: Returned when a pattern is found.
Common Metacharacters :
| Symbol | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| . | Any character except newline | a.c→abc |
| ^ | Start of string | ^Hello |
| $ | End of string | world$ |
| * | 0 or more occurrences | ba*→b,baaa |
| + | 1 or more occurrences | ba+→ba,baa |
| ? | 0 or 1 occurrence | ba?→b,ba |
| [] | Character set | [A-Z]or[a-z0-9] |
| {n,m} | Range | \d{2,4}→ 2 to 4 digits |
Common Regex Functions in Python
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| re.match() | Matches only at the start of the string | re.match(r”\d+”, “123abc”) |
| re.search() | Scans through the string for first match | re.search(r”cat”, “wildcat example”) |
| re.findall() | Returns all non-overlapping matches | re.findall(r”\d+”, “abc123def456”) |
| re.sub() | Replaces matches with given text | re.sub(r”[0-9]+”, “#”, text) |
| re.split() | Splits string by regex pattern | re.split(r”\s+”, “Hello World!”) |
Practical Examples of Regex in Python
Example 1: Extracting Emails from Text
import re
text = "Contact us at support@vbkinfo.xyz or admin@site.com"
emails = re.findall(r"[\w\.-]+@[\w\.-]+", text)
print(emails)
Output:
['support@vbkinfo.xyz', 'admin@site.com']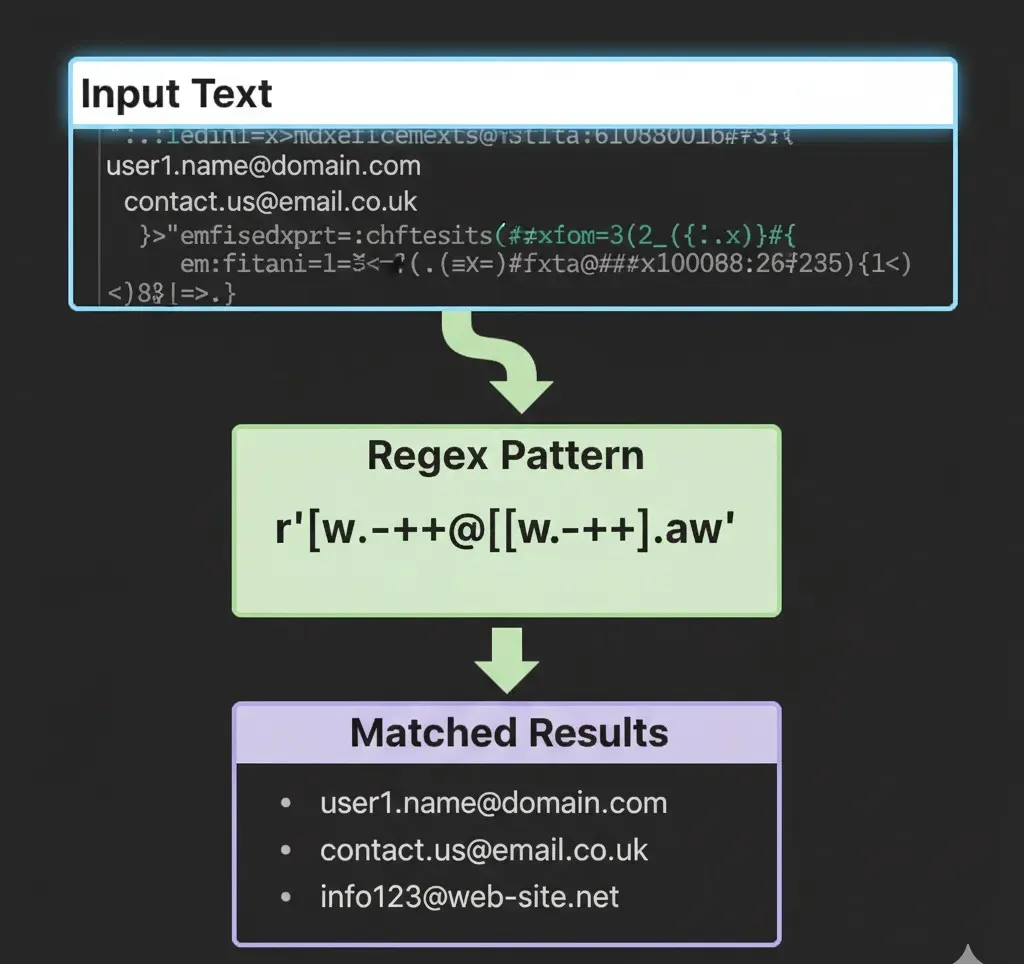
Example 2: Validating Usernames
pattern = r"^[A-Za-z0-9_-]{3,16}$"
usernames = ["vbk_dev", "John!", "user_123"]
for u in usernames:
print(f"{u}:", bool(re.match(pattern, u)))Output:
vbk_dev: True
John!: False
user_123: TrueExample 3: Replace Sensitive Words
text = "This password is 12345!"
cleaned = re.sub(r"[0-9]+", "####", text)
print(cleaned)Output:
This password is ####!Example 4: Case-Insensitive Search
re.search(r"python", "Learning PYTHON is fun", re.IGNORECASE)Output:
Match found successfully.
Real-World Analogy
Think of regex as a metal detector for text. Imagine you’re scanning a beach (the text) for coins (specific patterns). Regex lets you fine-tune how sensitive your detector is — only looking for gold coins (emails) or any metal object (any digits or words).
When you first start, the beeps might be confusing — but with practice, you’ll instantly notice the difference between useful finds and false alarms.
Tips, Tricks, and Common Mistakes
Tips
- Use raw strings: Always prefix patterns with
rto avoid escape confusion. - Test before coding: Use tools like regex101.com.
- Start simple: Build complex expressions step by step.
- Use comments: Add
(?x)flag for better readability.
Common Mistakes
- Forgetting to escape special characters (e.g.,
.matches anything, not a literal dot). - Overcomplicating patterns when simpler options exist.
- Ignoring performance — complex patterns can slow down big text scans.
FAQs / Interview Questions
- What is the difference between re.match() and re.search()?
re.match() checks only at the beginning of a string, while re.search() scans the entire string for a match. - How can you extract all digits from a text in Python?
Use re.findall(r”\d+”, text) — it returns all groups of digits. - What are greedy and non-greedy matches?
A greedy pattern (.) matches as much as possible, while non-greedy (.?) matches as little as possible. - How can regex be case-insensitive?
Add the re.IGNORECASE or re.I flag to your function call.
Comparison of Regex Methods
| Method | Checks Beginning Only | Finds All | Case Sensitive | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| match() | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | Start-only match |
| search() | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | First occurrence |
| findall() | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | All occurrences |
| sub() | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | Search & replace |
To master more Python tricks, check out our tutorials bellow:
for more deep dive into the python string then
Conclusion
Congratulations — you’ve just mastered the fundamentals and real-world power of Python regex. These patterns can appear intimidating, but with consistent use, your confidence and speed will grow.
Before you go:
- Revisit this guide when working on string manipulation.
- Try applying regex in web scraping or data cleaning tasks.
- Check out other advanced tutorials on vbkinfo.xyz Tutorials.
I’ve used regex for real-world Python projects involving log filtering, data validation in APIs, and cleaning CSV exports. The key learning — regex isn’t just for developers; it’s a real productivity hack for anyone dealing with messy text.